Quantitative biology & multidimensional imaging
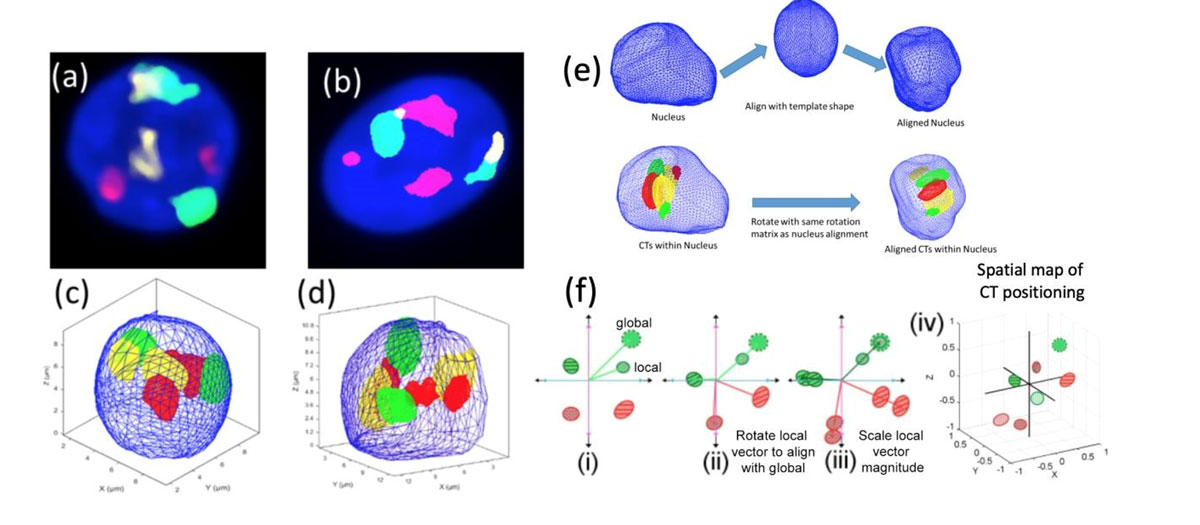
3D modelling for mapping the nuclear localization of genomic components using Spherical harmonics (SPHARM)
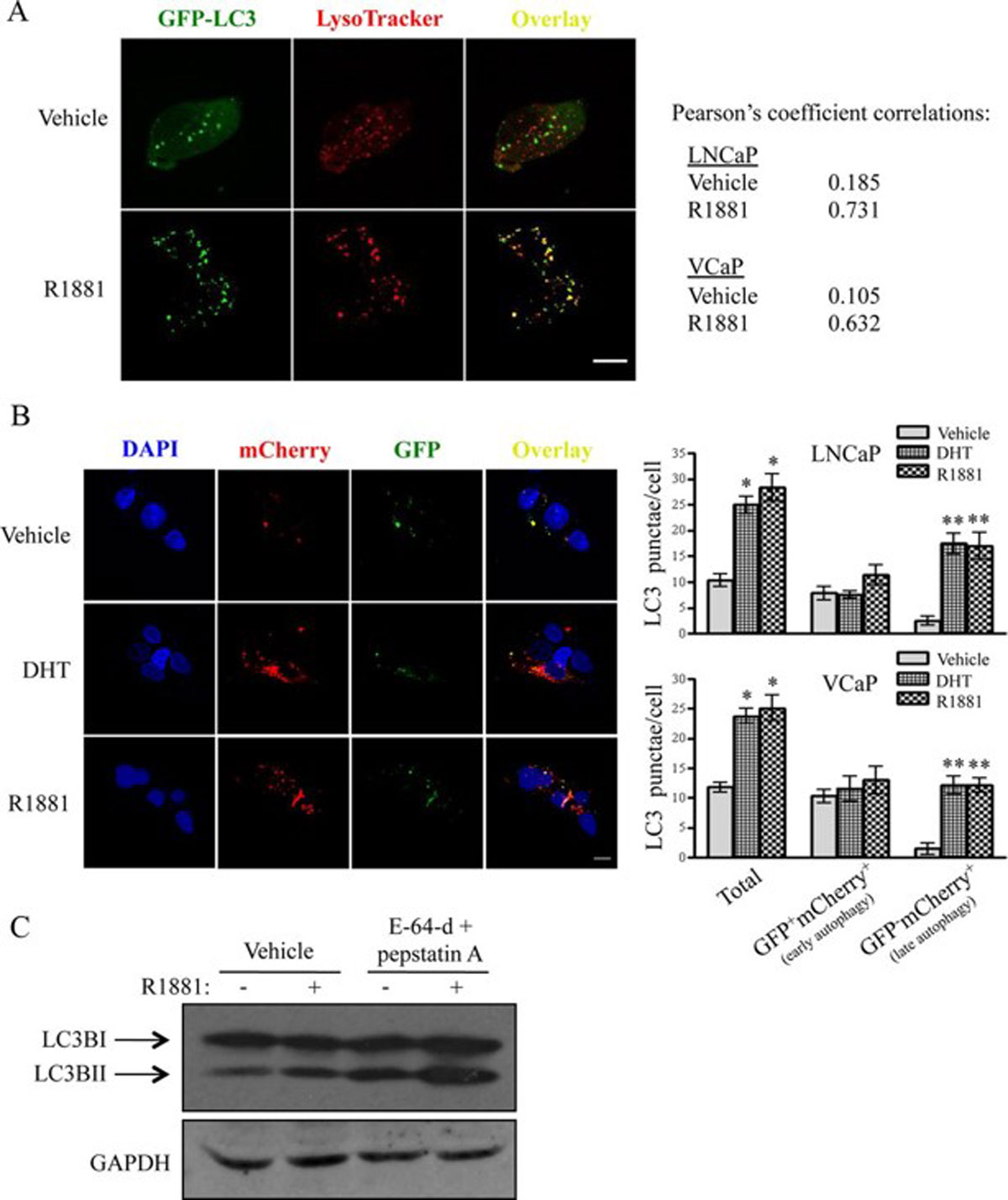
Analysis of co-localization and quantification of biomolecules in microscopy images
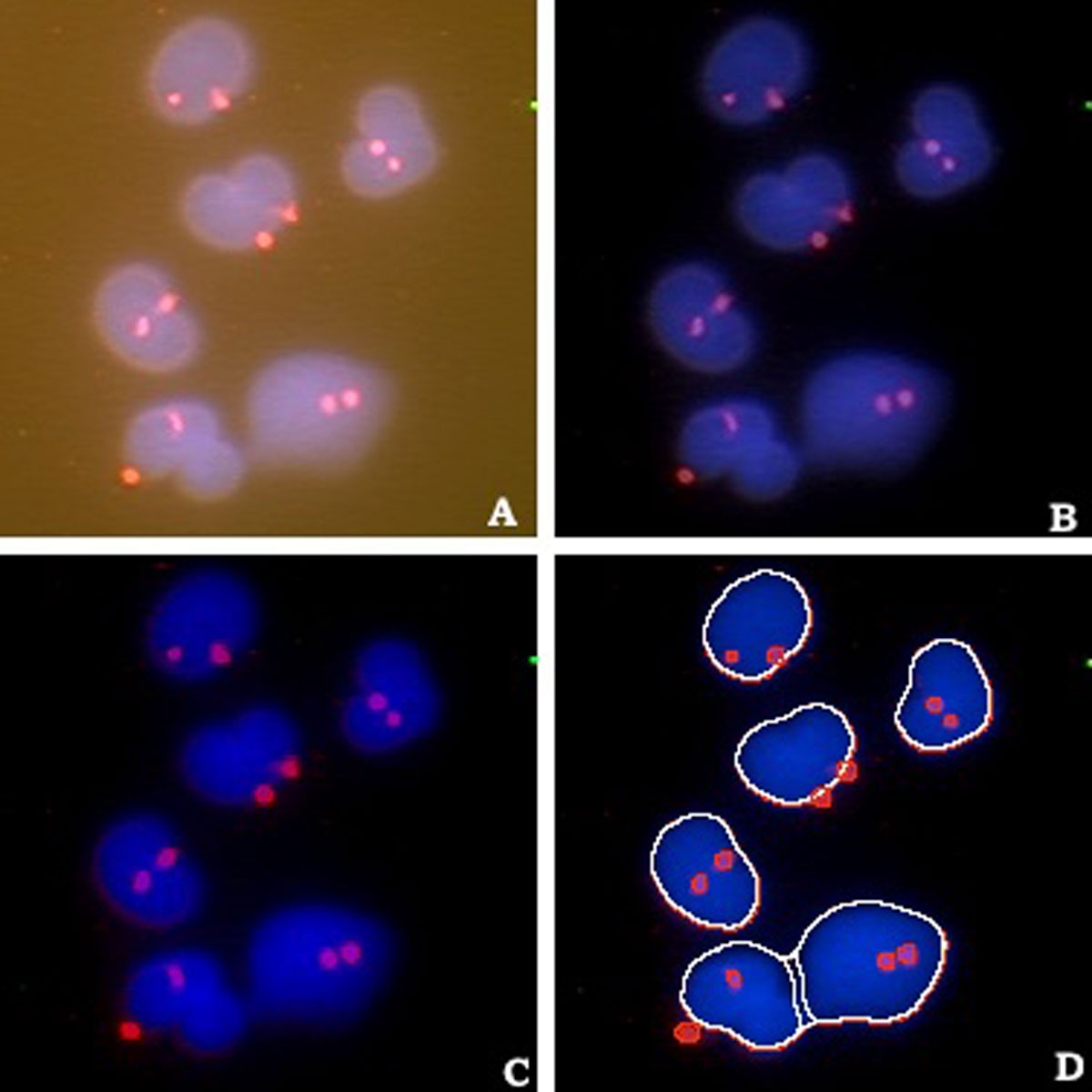
Computational cytometry